Publications

Tuberculosis (TB) is a major public health problem and the fourth leading cause of death in Kenya. Based on WHO End TB Strategy targets set in 2015, Kenya was among seven high TB countries that had achieved their first milestone of a 20% reduction in the TB incidence rate by 2021. An effective supply chain management system ensures a consistent and uninterrupted supply of TB medications and commodities. It ensures timely and accurate distribution of TB commodities while preventing stock-outs or shortages. Read more from the policy brief here:

?Now out! AFIDEP Newsletter, July – December 2023 AFIDEP News is the African Institution for Development Policy’s newsletter. It is published bi-annually to update stakeholders on our programmes. It highlights emerging policy issues in population dynamics, demographic dividend, health and well-being; transformative education and skills development; environment and climate change; gender equality, governance and accountability. This newsletter covers some of our work and impact in institutionalising use of evidence for the period running between June – December, 2023. To read the newsletter:

Multiple factors have been reported to drive the burden of TB among men globally, including behavioural factors such as tobacco smoking and alcohol consumption, social mixing, risky occupational exposures such as mining, and poor access to health services. These existing disparities pose a challenge to achieving broader progress towards global TB elimination, necessitating the identification of high-risk groups as the first step toward developing equitable policies and targeted interventions. Cross-sectoral collaboration among government agencies is essential to ensure synergy and complementarity in policies and strategies that are aimed at engaging men in TB programming. Read more from this evidence brief […]
Warning: Invalid argument supplied for foreach() in /home/daqh5xy6fshq/public_html/wp-content/themes/afidep2019/publications.php on line 53

AFIDEP work on governance and accountability has primarily been with African parliaments to institutionalise strategies that enable them to improve their oversight, representative and legislative functions. We now seek to step up this work by strengthening capacity for evidence-informed decision-making as a mechanism for enhancing better governance and accountability in service delivery and use of public resources. Our governance and accountability programme acknowledges the importance of the intersecting gender equality issues in governance. Read more about our impact in the brochure here:

Most African governments are not spending enough on health care. As a result, the Sustainable Development Goal 3 targets of universal health coverage and financial risk protection by 2030 are unlikely to be achieved. Without strong health systems, African countries are unlikely to make significant progress on persistent health challenges as well as emerging epidemics such as non-communicable diseases, antimicrobial resistance and neglected tropical diseases. Our health and wellbeing priority focus area seeks to provide capacity strengthening and technical assistance for evidence-informed decision-making. Find more details in the brochure here:

The devastating impacts and lessons learnt from other epidemic contexts show that health systems in low-income and middle-income countries (LMICs) and fragile and humanitarian contexts have a low capacity to implement an emergency response during disease outbreaks such as the COVID-19 pandemic caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus.1 2 Such unprecedented emergency and humanitarian situations burden health systems, which, even before the disease outbreak, have struggled to provide quality essential services. Very few studies have demonstrated how COVID-19 affects progress towards achieving sustainable development goals (SDGs), especially SDG number 3 in countries including Kenya and Ethiopia. In this study, we assessed […]
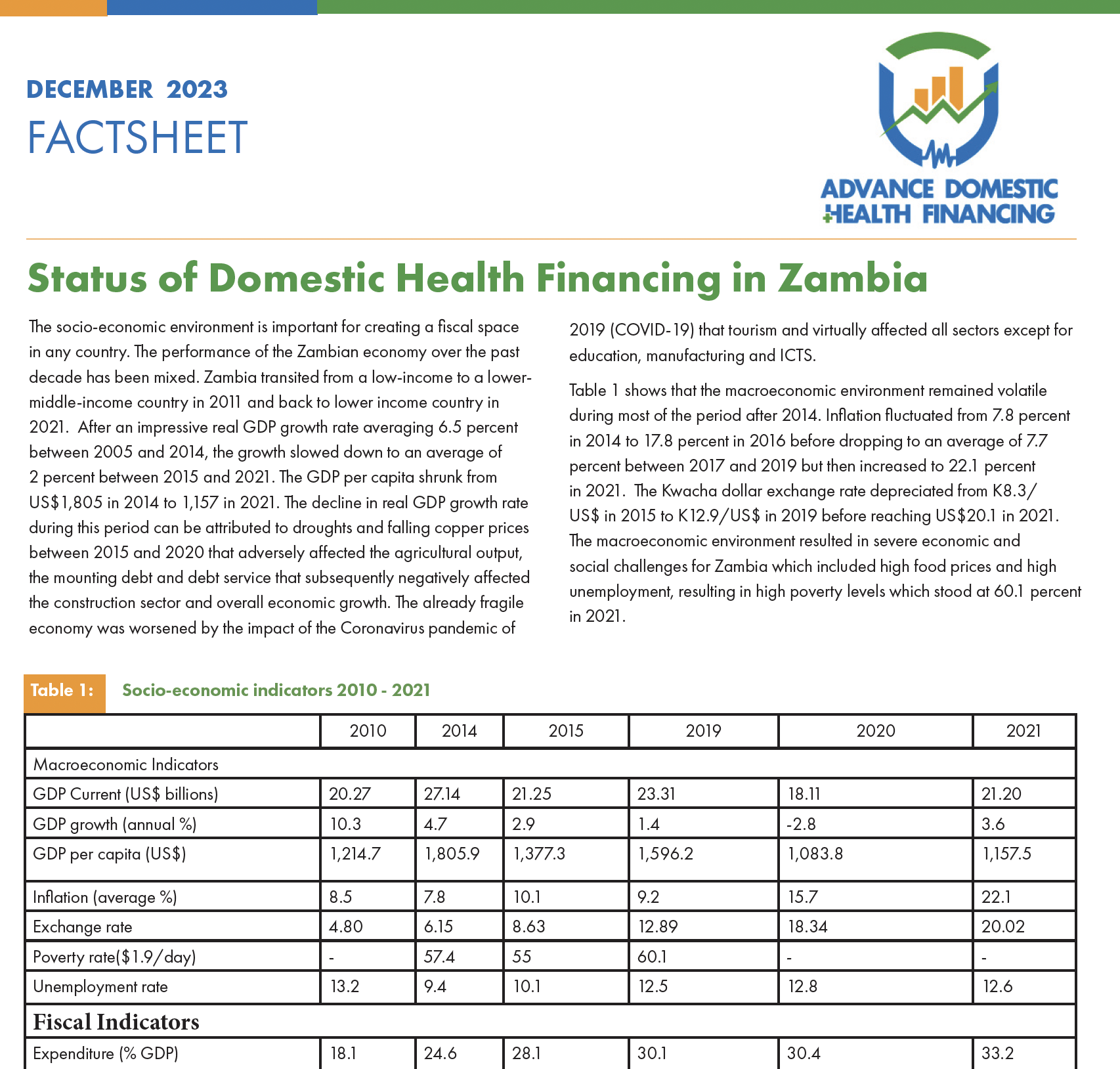
The socio-economic environment is important for creating a fiscal space in any country. The performance of the Zambian economy over the past decade has been mixed. Zambia transited from a low-income to a lower-middle-income country in 2011 and back to lower income country in 2021. After an impressive real GDP growth rate averaging 6.5 percent between 2005 and 2014, the growth slowed down to an average of 2 percent between 2015 and 2021. The GDP per capita shrunk from US$1,805 in 2014 to 1,157 in 2021. The decline in real GDP growth rate during this period can be attributed to […]
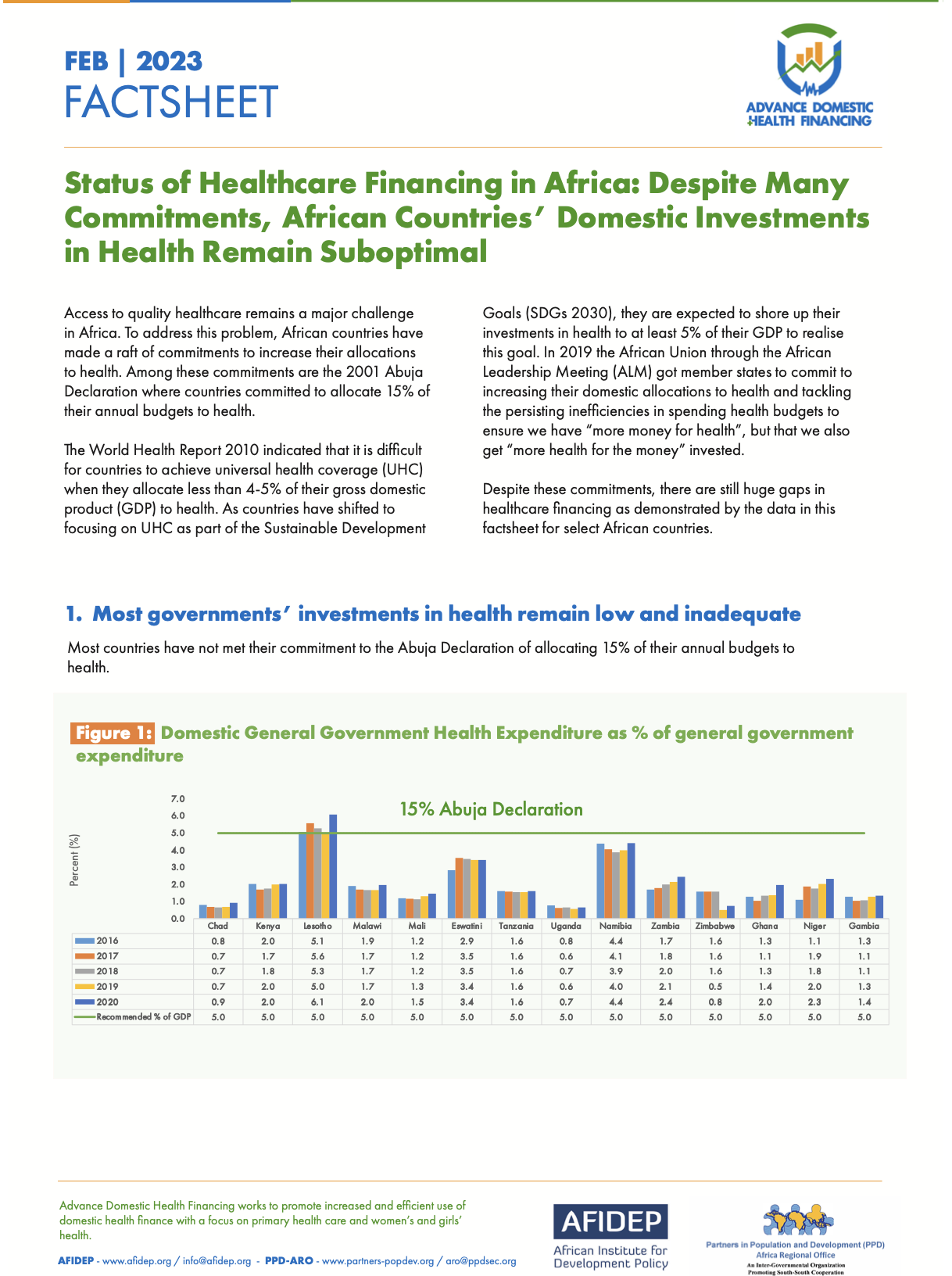
Access to quality healthcare remains a major challenge in Africa. To address this problem, African countries have made a raft of commitments to increase their allocations to health. Among these commitments are the 2001 Abuja Declaration where countries committed to allocate 15% of their annual budgets to health. The World Health Report 2010 indicated that it is difficult for countries to achieve universal health coverage (UHC) when they allocate less than 4-5% of their gross domestic product (GDP) to health. As countries have shifted to focusing on UHC as part of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs 2030), they are expected […]

The African Institute for Development Policy (AFIDEP), in partnership Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND) and Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology (JKUAT), conducted a policy review and analysis on Kenyan national diagnostics policies and plans to strengthen health systems in the country. Click here to read more.

Social health insurance (SHI) is a health finance mechanism that seeks to equitably protect people against financial and health burdens through risk pooling, which considers both the health risks of the people and the contributions by individuals, households, enterprises, and the government. SHI is being implemented in many countries as one of their main mechanisms for achieving universal health care (UHC). SHI typically has three characteristics: compulsory enrolment with members paying a specific premium; only those registered are entitled to benefits; and a legislation outlining the benefits members are entitled to for the premium amount they paid. Kenya is a […]

The Kenya Constitution of 2010 guarantees all Kenyan citizens a right to access the highest attainable standard of health, including reproductive health and emergency treatment. Kenya’s health sector is working towards achieving the Vision 2030 goal of universal health coverage (UHC), which should enable all individuals to receive equitable, affordable and quality health care without suffering financial hardship. Kenya has made strides towards achieving UHC and has made commitments that act as the steering wheel to achieve this goal. In 2015, all United Nations member states, including Kenya, committed to the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), with SDG 3 promoting […]

